The Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process is revolutionizing additive manufacturing. This technology enables the creation of complex geometries that were once impossible to achieve. According to industry reports, the market for this process is expected to reach $1.5 billion by 2026. However, there are challenges that require attention.
Quality control remains a critical issue. Inconsistent layer bonding can lead to defects in final products. Proper parameters must be established to ensure optimal energy inputs. Moreover, the right powder selection is essential. Different materials behave uniquely during laser fusion, impacting the overall outcome.
Operators must also consider their setup and environment. Variability in temperature can affect prints, leading to warping or inconsistent finishes. Continuous monitoring is key to mitigating these risks. While the potential of the Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process is immense, there is still much to learn and refine in this evolving field.
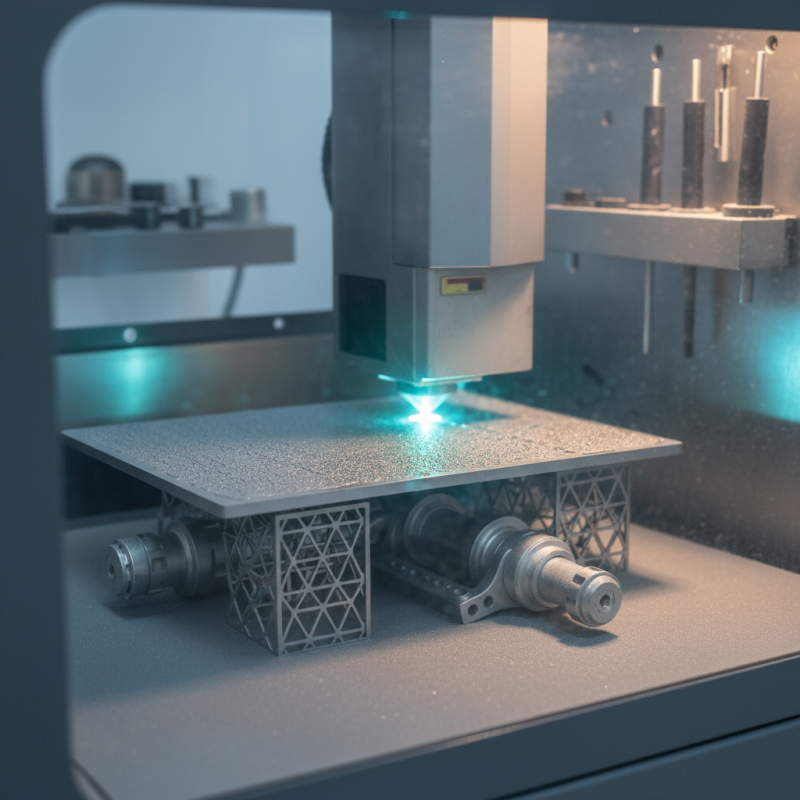
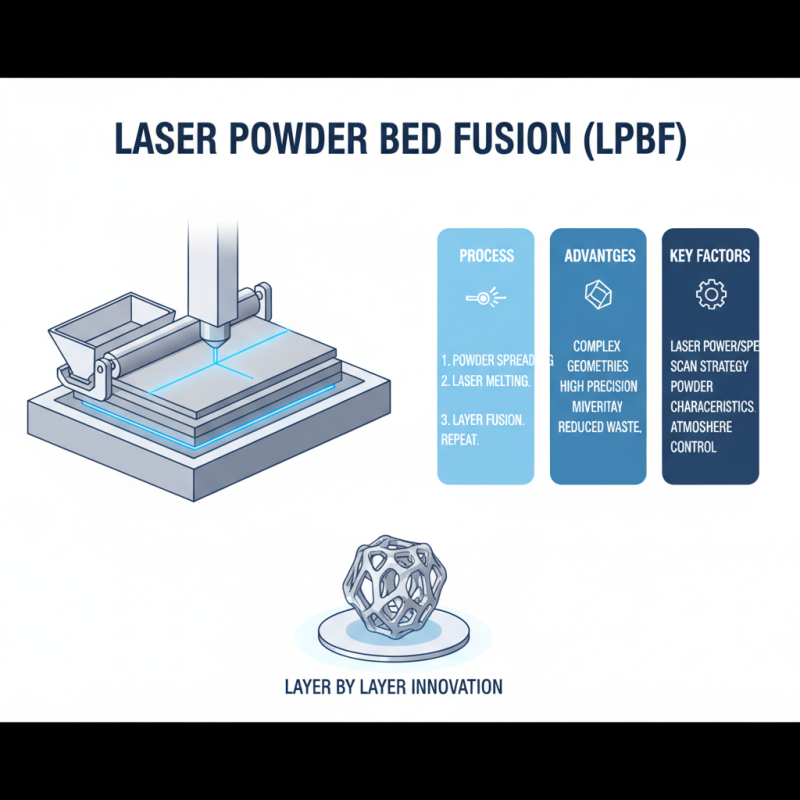
Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) is an advanced additive manufacturing technique. It utilizes lasers to melt powdered material, layer by layer. This process creates intricate designs and complex geometries. Each layer is precisely fused to the one beneath it. However, achieving optimal results involves careful attention to multiple factors.
Temperature control is crucial. High temperatures can lead to warping in the final product. Poor thermal management can also cause defects. The powder quality plays a significant role as well. If the powder is not uniform, it could result in weak spots in the structure. Inconsistent layer thickness further complicates the process.
Operators must also consider the laser parameters. The speed and power of the laser must be meticulously calibrated. Too high a power can cause excessive melting, while too low may not fuse the powder adequately. It's essential to experiment with these settings. Continuous refinement is part of the learning curve. Effective process monitoring is vital for identifying issues early. Each batch provides data for future adjustments. Embracing the inherent imperfections can drive innovation in LPBF techniques.
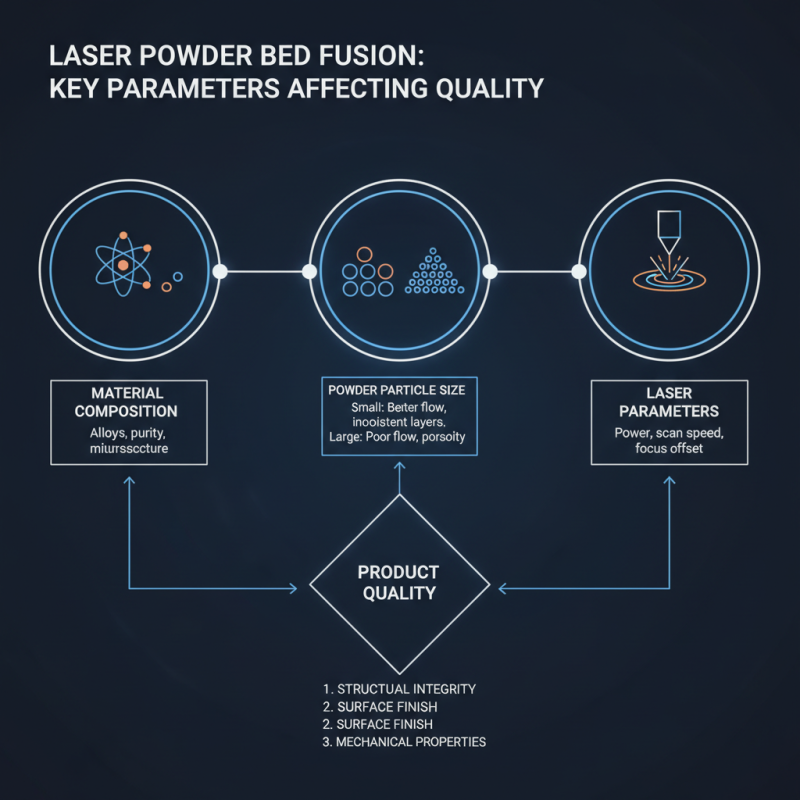
In the laser powder bed fusion process, several key parameters significantly affect the quality of the final product. The material composition plays a critical role. Variations in powder particle size can influence melt pool behavior. Smaller particles may result in better flowability, but they can also lead to inconsistent layer formation. This inconsistency may compromise structural integrity.
Laser power is another crucial variable. High power can increase melt depth, which could enhance bonding. However, excessive power can cause overheating. This leads to defects like porosity, negatively impacting mechanical properties. Additionally, the scanning speed needs careful adjustment. Faster speeds might reduce energy input but risk insufficient melting of the powder layers.
Temperature control in the build chamber also matters. A uniform temperature can minimize warping, but too much heat can degrade the material. In some cases, the use of inert gases helps maintain an ideal environment. While aiming for optimal parameters may yield better results, slight deviations can reveal areas for improvement. Reflection on these factors is essential for enhancing the overall process and product quality.
Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) is a groundbreaking technology in additive manufacturing. The choice of materials greatly influences the success of this process. Common materials include stainless steel, titanium alloys, and aluminum. Each material has unique properties, making them suitable for different applications.
Stainless steel is often chosen for its strength and corrosion resistance. However, it can be challenging to optimize its print settings.
Titanium alloys are lighter and stronger but tend to be more expensive. The difficulty in their processing can lead to defects if not handled correctly.
Aluminum, while known for its lightweight, can also have issues with warping during the cooling process.
The selection of materials must be based on the desired application. Engineers may find it difficult to strike the right balance between performance and cost. Understanding how to manipulate each material's properties is key. There is much to learn from both successes and failures in LPBF projects. Each attempt offers insights that can drive innovation and refine techniques further.
Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) is gaining attention in advanced manufacturing. Inspection and quality control are critical to ensure product reliability. Studies indicate that nearly 30% of defects in LPBF components arise from inadequate quality checks.
One effective method is in-situ monitoring during the build process. Utilizing optical cameras and thermal sensors can identify deviations in layer formation. This allows for immediate adjustments. However, not all companies adopt this technology due to costs and complexity. Proper training is essential for personnel operating these systems.
Tip: Regularly calibrate your monitoring instruments. This ensures accurate readings and reliable data.
Post-build inspections are equally vital. Techniques like X-ray computed tomography (CT) are used to detect internal defects. Research shows that CT inspections can detect up to 95% of potential failures. Yet, some organizations overlook this step, relying solely on visual inspections.
Tip: Incorporate a routine schedule for CT inspections to avoid hidden issues.
The LPBF process involves many challenges. Sometimes, defects might not be visible until after production. This often leads to costly waste. Continuous improvement in quality control practices can mitigate risks, ensuring high-quality outputs.
Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) is evolving rapidly, with many innovations shaping its future. One significant trend is the integration of artificial intelligence. AI can optimize layer parameters, leading to enhanced build quality. However, our trust in AI must be approached critically. Over-reliance on algorithms may obscure crucial human insights.
Additive manufacturing materials are also advancing. New alloys and powders are enhancing the performance of LPBF. These materials can significantly improve thermal properties, but their costs may pose challenges. This constant evolution requires constant evaluation of material efficacy versus expense.
Lastly, sustainability is becoming a priority. The focus on recycling powder and reducing waste is commendable. Yet, the practical implementation of these methods often falls short. Balancing innovation with real-world application is an ongoing struggle. The future of LPBF holds great promise, but careful consideration is necessary for true advancement.