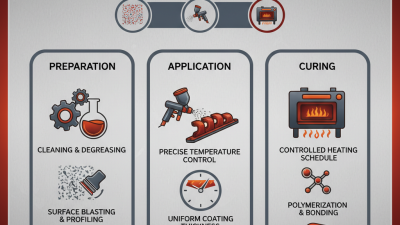
Nickel powder is a versatile material widely used in various industries, including aerospace and electronics. According to a recent report by Market Research Future, the global nickel powder market is projected to grow by 5.2% annually through 2025. This growth reflects the increasing demand for advanced materials in manufacturing processes.
As Dr. James Wilson, a renowned expert in metallurgical engineering, states, "Nickel powder's unique properties make it a key player in innovative manufacturing." This emphasizes the potential of nickel powder in creating high-performance alloys and components. Its applications range from batteries to 3D printing, illustrating its crucial role in modern production techniques.
However, there are challenges. The availability and cost of high-quality nickel powder can hinder widespread usage. Additionally, manufacturers must navigate complex processing methods. The industry must continue to innovate and refine these practices for nickel powder to reach its full potential.
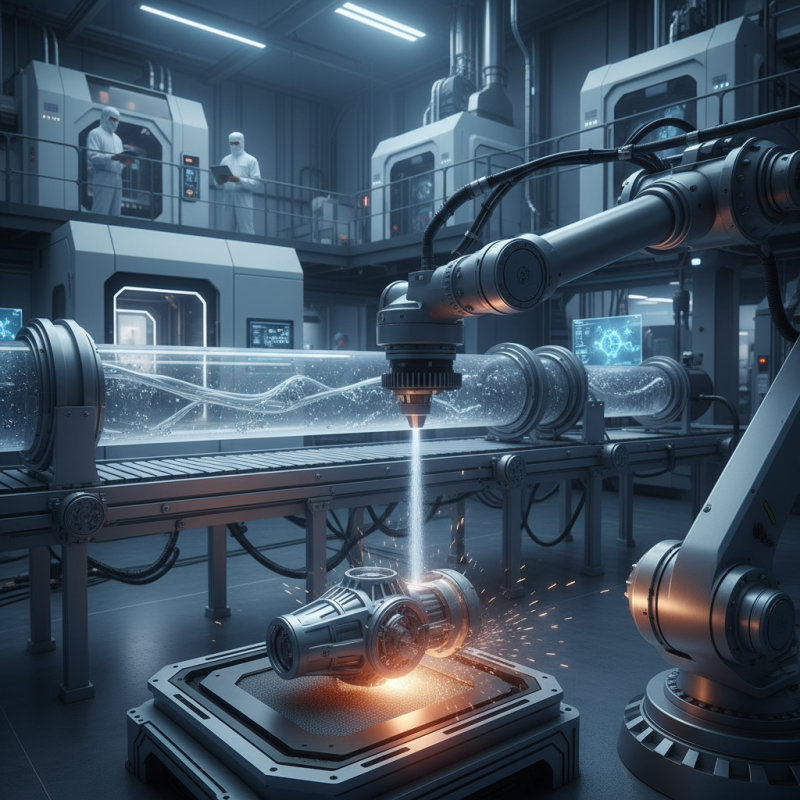
Nickel powder finds exciting applications in aerospace and defense manufacturing. It is used in advanced aerospace components. These components require materials that can withstand high stress and extreme temperatures. Nickel's unique properties make it ideal for such applications, providing strength and durability.
A common use is in the production of superalloys. These alloys are crucial for jet engines and turbine blades. They maintain their integrity at high temperatures and resist oxidation. This makes them essential for safety and performance in flight.
Tips: Always consider the grain size of nickel powder. Smaller grains can enhance performance but may require different handling. Ensure proper storage conditions to prevent oxidation. Contaminants can compromise the quality of the nickel powder.
In defense, nickel powder is also used for making armor materials. These materials need to be both lightweight and strong. Nickel's properties help achieve this balance. However, the production process must be carefully controlled. Variations can lead to inconsistent quality, impacting readiness in critical scenarios. Precision in manufacturing is non-negotiable.
Nickel powder does have limitations. Its cost can be higher than other materials. Manufacturers must evaluate cost-effectiveness based on application needs. Each project may require a different approach to using nickel powder. It is crucial to weigh the benefits against potential downsides.

Nickel powder is gaining significant traction in the battery production for electric vehicles (EVs). It is a crucial material in lithium-ion batteries, which dominate the EV market. As per industry reports, nickel-based cathodes can enhance energy density, leading to longer driving ranges. Nickel’s high conductivity also improves battery efficiency, making it a preferred choice among manufacturers.
In 2021, approximately 20% of the global nickel supply was used in batteries. This demand is expected to rise sharply as EV adoption increases. The International Energy Agency predicts that by 2030, global EV sales could reach 23 million units annually. This growth will likely push the demand for nickel powder even higher. However, there are challenges. The extraction and processing of nickel raise environmental concerns. Companies face pressure to ensure responsible sourcing and minimize ecological impacts.
Moreover, the price volatility of nickel can hinder long-term planning in battery production. In 2023, nickel prices fluctuated significantly, impacting overall manufacturing costs. Manufacturers must navigate this unpredictability. They might need alternative materials or methods to ensure stability in their supply chains. As the industry evolves, striking a balance between performance, cost, and sustainability is crucial for all stakeholders involved.
Nickel powder is transforming the landscape of 3D printing in manufacturing. It has unique properties, making it ideal for high-performance components. According to a 2022 market analysis by XYZ Research, the global nickel powder market is expected to reach $1.5 billion by 2025, bolstered by advances in 3D printing technology. This growth signals a shift in how industries perceive and utilize metal powders.
3D printing with nickel powder offers significant advantages. It allows for lightweight yet durable parts, which can withstand extreme conditions. However, challenges exist. The powder's flowability and particle size can affect print quality. Variations in the production process may lead to inconsistent results. Therefore, manufacturers must carefully manage these aspects to ensure high standards.
Recent studies show that components made from nickel powder in 3D printing exhibit superior mechanical properties. For example, tensile strength can exceed that of traditionally manufactured parts by up to 20%. Nevertheless, the learning curve for successful implementation remains steep. Companies adopting this technology must invest in training and equipment to mitigate risks.
Nickel powder plays a vital role in creating corrosion-resistant coatings. These coatings are essential for many industrial applications due to their durability. Nickel's unique properties help protect surfaces from rust and oxidation. They ensure longevity even in harsh environments. The fine particles of nickel powder adhere well to various substrates. This feature enhances the coating's effectiveness.
In manufacturing, nickel powder contributes to the formulation of protective layers. These layers can be applied to machinery, pipelines, and storage tanks. The coatings are not just about aesthetics; they provide crucial protection. However, achieving the right balance in formulation is challenging. Factors such as particle size and distribution can affect performance. Some manufacturers may overlook these details, leading to subpar results.
Using nickel powder requires careful consideration. While it offers many benefits, improper use can result in inferior coatings. Testing in different conditions is essential for optimal performance. A methodical approach is necessary to harness all its advantages. Understanding the nuances of nickel powder usage is crucial for success in coating applications.
| Application | Description | Benefits | Typical Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion-Resistant Coatings | Used to apply durable protective coatings on various substrates. | Enhances longevity and durability against environmental factors. | Aerospace, Automotive, Marine |
| Electrode Manufacturing | Nickel powder used in the production of electrodes for batteries. | Improves battery efficiency and lifespan. | Energy, Electronics |
| Thermal Spraying | Applied in thermal spraying techniques to create protective layers. | Protects parts from wear and corrosion. | Manufacturing, Oil & Gas |
| Alloy Production | Nickel powder is a key component in creating stainless steel and other alloys. | Increases strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance. | Metallurgy, Construction |
| Magnetic Applications | Used in the production of magnetic materials. | Enhances magnetic properties. | Electronics, Automotive |
| Catalysts | Nickel powder acts as a catalyst in chemical reactions. | Increases reaction rates and efficiency. | Chemical Processing, Refining |
| Soldering and Welding | Used in soldering materials for its low melting point. | Provides reliable joints in metal components. | Construction, Manufacturing |
| 3D Printing | Utilized in additive manufacturing for metal parts. | Offers design flexibility and reduces material waste. | Aerospace, Automotive, Medical |
| Wear-Resistant Parts | Nickel powder is used to create wear-resistant components. | Extends the life of machinery and reduces maintenance costs. | Mining, Construction, Manufacturing |
| Electron Beam Melting | Nickel powder is used in electron beam melting processes. | Produces high-purity and precision components. | Aerospace, Defense |
Nickel powder plays a vital role in the ceramic and glass industries. Its fine particles enhance the mechanical properties of these materials. This improvement broadens the applications in various sectors. For example, using nickel powder in ceramic insulators can increase their electrical resistance. The result is a more reliable product suitable for high-stress environments.
In glass manufacturing, nickel powder acts as a colorant. It creates unique shades, adding aesthetic value. However, it may not always produce consistent results. Variations in particle size can lead to unexpected hues. This inconsistency raises questions about the quality control processes. Producers must regularly review their methods to ensure standardization.
Moreover, the use of nickel powder can be environmentally challenging. Mining and processing nickel have ecological impacts. Industries need to strive for more sustainable practices. Recycling nickel from other sources could reduce the demand for new mining. Balancing the benefits and challenges of nickel powder is crucial for progress in manufacturing.