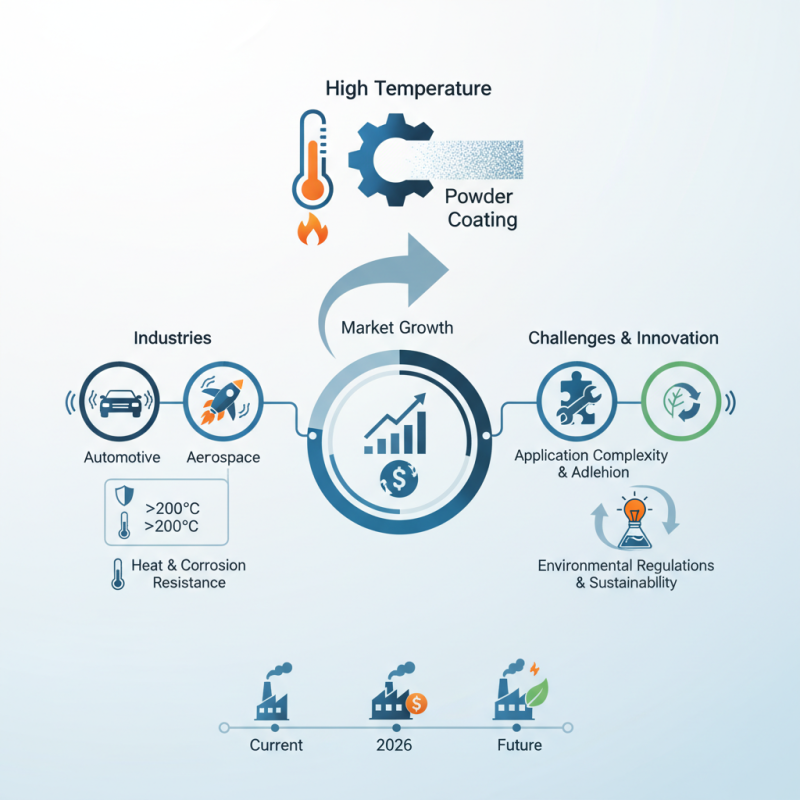
High Temperature Powder Coating has gained significant traction in various industries. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global powder coating market is projected to reach $12 billion by 2026. This growth is driven by the demand for high-performance coatings that can withstand extreme environments. High Temperature Powder Coating specifically addresses this need, offering durability and resistance to thermal degradation.
The application of High Temperature Powder Coating is evident in sectors such as automotive and aerospace. These industries require coatings that can endure intense heat and corrosion. For instance, the automotive sector increasingly uses these coatings on exhaust components. Their ability to withstand temperatures above 200°C makes them indispensable. However, the technology is not without challenges. The complexity of application and potential issues with adhesion require careful consideration.
While High Temperature Powder Coating serves many purposes, it also necessitates ongoing innovation. Manufacturers must adapt to evolving environmental regulations and sustainability demands. The ongoing quest for improved performance and lower environmental impact highlights the need for research and development. This evolving landscape presents both opportunities and challenges for industry players.
High temperature powder coating is a specialized process designed for applications requiring durability in extreme environments. This technique involves applying a dry powder to a substrate, which is then heated to create a robust finish. According to the Powder Coating Institute, coatings can withstand temperatures up to 400°F or more, making them ideal for automotive and industrial applications.
The process of high temperature powder coating is intricate. A powder blend is electrostatically charged, allowing it to adhere to the surface of the item. Once the coating is applied, it's baked in an oven, where the heat causes the powder to melt and cure. This creates a strong, continuous finish that protects against corrosion, UV rays, and mechanical wear. However, achieving the perfect layer requires careful control over temperature and application settings. Missteps can lead to imperfections or uneven coatings.
Data from industry reports highlights that nearly 70% of high temperature coatings meet stringent standards for performance. Yet, challenges remain. Variability in substrate material and environmental conditions can affect the end result. Operators must frequently adjust their methods. Continuous improvement in the application process and formulation is essential to address these issues. High temperature powder coating is a fascinating field, balancing innovation and practical challenges in coating technology.
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Coatings that can withstand high temperatures, typically up to 450°C (840°F). | Durability and longevity in extreme heat environments. | Automotive parts, industrial equipment, and exhaust systems. |
| Process | Involves electrostatic application of powder followed by curing in an oven. | Uniform coating and reduced hazardous waste. | Furnaces, grills, and other high-temperature components. |
| Material Composition | Formulated using resins and additives specifically designed for high heat application. | Enhanced performance and chemical resistance. | Aerospace and electrical components. |
| Color and Finish | Available in various colors and finishes, including textured and glossy options. | Aesthetic versatility while maintaining performance. | Home appliances and decorative fixtures. |
High temperature powder coating is gaining traction in industrial applications for several reasons. This technique allows for durable, high-performance finishes that can withstand extreme conditions. Industries often face demanding environments, from automotive to aerospace. The resilience of high temperature coatings helps to extend the lifespan of parts and reduce maintenance costs.
One key benefit is their superior adhesion. High temperature powder coatings bond effectively to various surfaces, providing long-lasting protection. This results in enhanced resistance to corrosion and chemicals. Furthermore, the coatings can endure higher temperatures without degrading, making them ideal for components exposed to heat. Enhanced aesthetic appeal is another advantage. These coatings come in various colors and finishes, improving the visual aspect of industrial parts.
Tips: Ensure proper surface preparation for the best results. Any contaminants can affect adhesion and performance. Always follow application guidelines closely. Cure times and temperatures are crucial for achieving optimal outcomes. Make adjustments based on equipment and environment to avoid common pitfalls. Consider conducting small test applications before full-scale production. This can help identify potential issues early on.
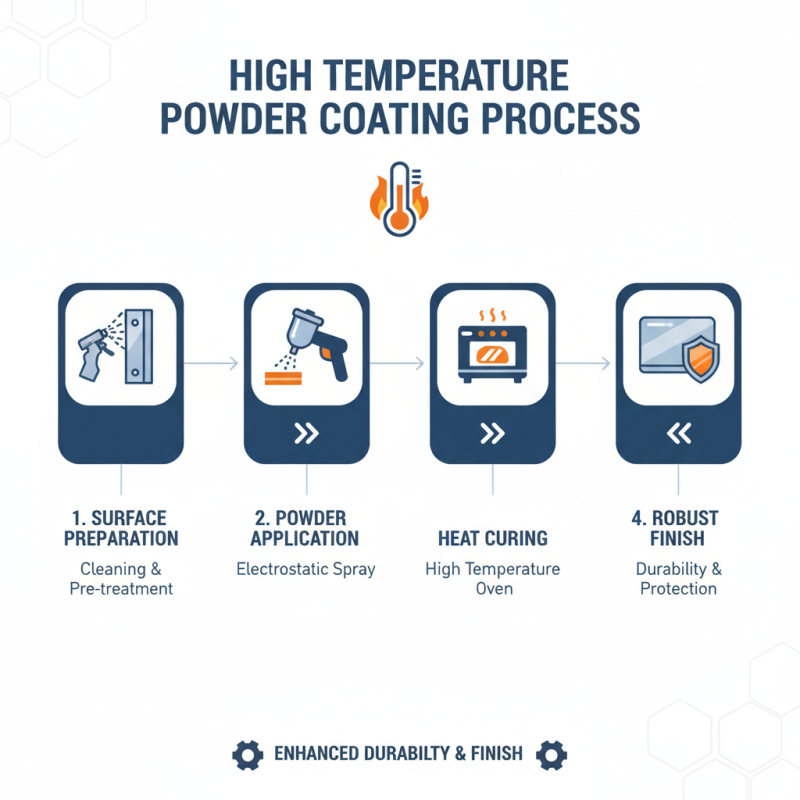
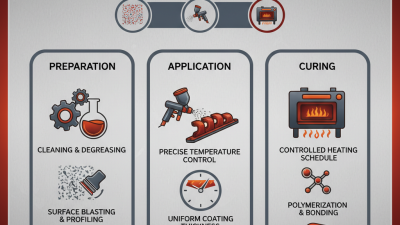
High temperature powder coating is a specialized process designed to enhance durability and finish. This technique applies a powder to a surface that then undergoes a curing process through heat. The steps in this process are crucial for achieving a robust finish.
To begin, the surface must be thoroughly cleaned. Dirt and grease can compromise adhesion. This is often a tedious task but essential for quality results. After cleaning, the powder is electrostatically charged. This charging allows the powder to cling to the surface effectively. It's a fascinating interaction between electricity and the powder particles.
Once coated, the item is placed in an oven. The temperature usually ranges from 350 to 400 degrees Fahrenheit. This heat melts the powder, transforming it into a smooth, uniform layer. Observing the transformation can be quite exciting. However, if not monitored closely, the coating may bubble or burn. Therefore, timing and temperature are critical considerations during this stage. Understanding these nuances can greatly influence the outcome, making this process both an art and a science.
High temperature powder coating is a specialized process designed to enhance the durability of various materials. When selecting powders for high temperature applications, it’s crucial to consider their composition and performance under extreme conditions. Common materials used include epoxy, polyimide, and silicone-based powders. These powders can withstand elevated temperatures exceeding 400°F (204°C) without degrading, as reported by the Powder Coating Institute.
Epoxy powders are often favored for their strong adhesion and corrosion resistance. However, they may lose some flexibility at high temperatures. Polyimide powders, on the other hand, offer superior thermal and chemical resistance, making them ideal for aerospace and industrial applications. Silicone-based powders provide excellent weatherability, but they may have limited hardness compared to other options.
**Tips:** When choosing a powder, check the specific temperature limits. Ensure proper surface preparation for better adhesion. Consider testing on a small scale before large applications to identify potential issues. Adapting your approach based on feedback is essential for achieving optimal results. While powders can be robust, imperfections may arise, prompting a reevaluation of material choices. Continuous improvement helps in refining the coating process and enhancing product quality.
Quality control is essential in high temperature powder coating production. This process involves multiple stages that require precise monitoring. Incoming raw materials must be tested for quality before use. Even small variances can lead to flaws in the final product.
During the coating application, it's crucial to maintain the right conditions. Temperature and humidity play significant roles. If these factors are off, it may affect adhesion. It's not uncommon for batches to fail due to overlooked details. Regular calibration of equipment is vital but can often be underestimated.
After the curing process, inspection is essential. Visual checks and adhesion tests can reveal defects. It's important to have a structured feedback loop. Teams should document challenges and solutions for future reference. Learning from past mistakes can enhance overall quality control measures. This ongoing reflection helps streamline the production process.