In modern industry, Powder Metals play a crucial role in shaping advanced manufacturing processes. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in Powder Metallurgy, "The versatility of Powder Metals transforms traditional manufacturing." This statement encapsulates the significance of Powder Metals in various applications today.
The market for Powder Metals is evolving rapidly. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices are increasingly adopting these materials. Manufacturers are drawn to their ability to create complex geometries and reduce material waste. Moreover, Powder Metals offer superior performance in high-temperature environments.
However, the journey isn't without challenges. Sourcing high-quality powders can be difficult. Additionally, not all Powder Metals are suitable for every application. The importance of ongoing research and development cannot be overstated. Companies must continuously adapt to new technologies and market demands. As we delve into the top applications of Powder Metals, we must reflect on both their potential and limitations.

Powder metallurgy is a vital process in modern industry. It involves creating metallic parts from fine powders. This technique offers unique advantages. Lower material waste is one of them. The process also allows for complex shapes that traditional methods struggle to achieve.
Various industries use powder metals. Automotive manufacturing is a key sector. Engine components made using this method are lighter. This improves fuel efficiency. Aerospace applications benefit too. Components can withstand extreme conditions. However, not every application is perfect. Some parts may face durability issues under stress. Understanding these limitations is essential for progress.
Innovation continues to shape powder metallurgy's future. Research explores new materials and techniques. The industry must adapt to changing demands. An evolving landscape presents challenges but also opportunities. Energies must focus on refining processes. Better quality and performance are the goals. Each step forward brings potential, but also questions about sustainability and efficiency.
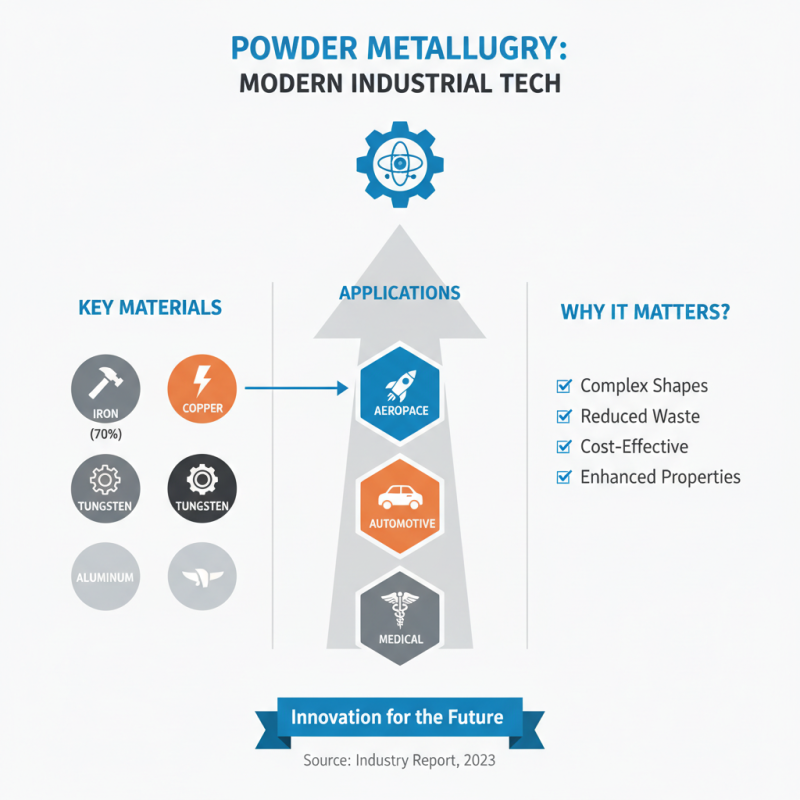
Powder metallurgy is a key technology in modern industry. Various powder metals are utilized across multiple sectors, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical. Key materials include iron, copper, tungsten, and aluminum. Iron powder remains the most widely used. It accounts for approximately 70% of the total market volume. Copper powders find applications in electrical components due to their excellent conductivity.
In terms of applications, the automotive industry heavily relies on powder metals for making gears, bearings, and structural parts. According to recent industry reports, the aerospace sector's demand for high-performance materials is driving innovations in titanium and nickel-based powders. These materials offer high strength and corrosion resistance, crucial for engines and frames.
**Tip:** When selecting powder metals, consider their flow characteristics and compaction behavior.
Some challenges arise in the processing of these materials. Depending on the powder's size and morphology, inconsistencies can occur during production. This could lead to defects in the final product.
**Tip:** Conduct thorough testing on powder properties to ensure quality.
Overall, understanding the types of powder metals and their unique characteristics is vital for enhancing product performance. Each application may require different properties, so it's crucial to reflect on specific needs before choosing a material.
Powder metallurgy (PM) is changing modern manufacturing. The ability to create complex shapes with high precision is a significant advantage. According to a report by the Metal Powder Industries Federation, PM components can achieve tighter tolerances than traditional methods. This precision allows for reduced waste and cost efficiency.
The materials used in powder metallurgy enhance product performance. For instance, parts made from PM often exhibit better strength and wear resistance. Studies indicate that PM components can have up to 30% greater density than those made from conventional methods. This density increases durability, making parts suitable for demanding applications in automotive and aerospace industries.
However, the process is not flawless. Challenges include controlling the quality of powder and achieving uniform compaction. Variation in powder quality can lead to defects in the final product. Continuous improvements in technologies are necessary to overcome these issues. Investors should weigh these challenges against the benefits of adopting powder metallurgy in their manufacturing processes.
The automotive and aerospace sectors are seeing a surge in the use of powder metals. These materials offer unique properties, such as high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent resistance to heat. They allow manufacturers to create complex shapes that traditional fabrication methods struggle with. For instance, components like turbine blades can be produced with intricate cooling channels, enhancing efficiency.
Tips: Focus on choosing the right powder for your application. Each metal behaves differently. Some may require a more careful handling process, which can complicate production.
Lightweight components are crucial for fuel efficiency. Powder metals reduce the overall weight of vehicles and aircraft. Yet, producing these metals often involves several steps that may not be well understood. The sintering process, for example, can lead to inconsistencies. Understanding these nuances is vital for successful integration.
Tips: Experiment with different sintering temperatures. This can impact the final product's quality significantly. Small changes can lead to major improvements or failures. Consider collaborating with specialists when venturing into this field.
This bar chart illustrates the market share of various applications of powder metals in modern industry, highlighting their significant roles in automotive parts, aerospace components, medical devices, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment.

The landscape of powder metal technology is continuously evolving. Researchers are exploring new materials and processes to enhance performance. Innovations in additive manufacturing are a significant trend, enabling complex geometries. This method reduces waste and allows for unique designs in various applications.
Another essential development is the integration of smart technologies. Sensors embedded in powder metals provide real-time data. This enhances quality control during production. Yet, challenges remain in standardization and scalability. The industry must address these issues to fully harness smart technologies' potential.
Sustainability has become increasingly important in powder metallurgy. Many manufacturers are seeking eco-friendly practices. This includes recycling metal powders and reducing energy consumption. However, balancing performance with sustainability remains a difficult task. Future advancements must focus on achieving this equilibrium.