In the realm of manufacturing and design, the utilization of metallic powders has gained significant attention due to their versatility and unique properties. These fine particles play a crucial role across various applications, from advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D printing to traditional metalworking processes. Their ability to influence the mechanical, optical, and thermal characteristics of end products makes understanding the different types of metallic powders essential for anyone engaged in industrial projects.
Whether you are a seasoned professional or a newcomer to the field, familiarity with the top metallic powders available can enhance your project outcomes. Each type of metallic powder offers distinct advantages that cater to specific requirements, such as weight reduction, strength enhancement, and conductivity. As we explore the top 10 metallic powders you need to know, we aim to illuminate their properties, applications, and the science behind their effectiveness, providing you with a foundational understanding that can elevate your projects to new heights.

Metallic powders are fine particles made from metals that have a wide range of applications across various industries. These powders are valued for their unique properties, such as conductivity, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. In manufacturing, metallic powders are extensively used in processes like additive manufacturing (3D printing), where they enable precise and complex geometries that traditional machining may struggle to achieve. Additionally, they play a critical role in powder metallurgy, allowing for the production of components with superior mechanical properties through processes like sintering.
Beyond industrial applications, metallic powders are also found in the realm of art and design. Artists and designers utilize these materials to create striking visual effects in sculptures, prints, and coatings. The reflective quality of metallic powders provides a vibrant flair, making them a popular choice for decorative finishes in products ranging from automotive paints to home furnishings. Furthermore, with advancements in technology, there is a growing trend to explore innovative ways to utilize metallic powders in electronics and renewable energy, signaling a promising future for these versatile materials.
When selecting metallic powders for your projects, understanding their key properties is essential. The particle size distribution, for instance, can significantly affect the flowability and packing density of the powder, leading to variations in the final product's mechanical properties. Finer particles generally provide better surface finish and finer detail in applications such as 3D printing and powder metallurgy, while coarser powders might be more suitable for applications requiring higher density or mechanical strength.
Another crucial property to consider is the chemical composition of the metallic powder. Different alloys and metals can offer varying degrees of corrosion resistance, conductivity, and thermal properties. For example, powders of stainless steel may be used where rust resistance is crucial, while copper powders are preferred in applications requiring excellent electrical conductivity. Additionally, the purity of the powder can influence the performance and longevity of the final product, making it vital to assess the material specifications relative to the intended application. Understanding these properties will help ensure optimal performance and durability in your projects.
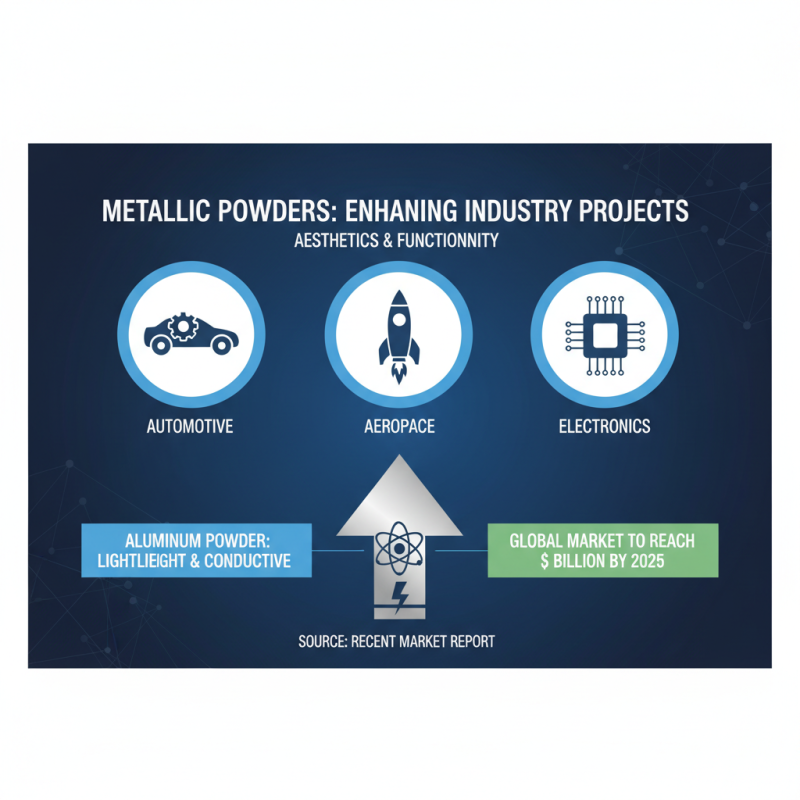
When it comes to enhancing the aesthetics and functionality of projects across various industries, metallic powders play a crucial role. These materials are characterized by their unique properties, making them essential for applications in automotive, aerospace, and electronics sectors. For example, aluminum powder is renowned for its lightweight characteristics and excellent conductivity, making it ideal for manufacturing lightweight components without compromising performance. According to a recent market report, the global aluminum powder market is projected to reach USD 1 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand in diverse applications.
Another noteworthy metallic powder is copper powder, celebrated for its high thermal and electrical conductivity. It is extensively utilized in manufacturing conductive inks and as a catalyst in chemical reactions. The global copper powder market is expected to grow significantly, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.6% from 2020 to 2027. Additionally, nickel powders are earning attention for their corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, making them suitable for diverse industrial applications including coatings and batteries. Data from industry analysts indicate that the demand for nickel powders is set to increase, especially in battery technology, which is anticipated to witness exponential growth in the coming years.
The distinct characteristics of these metallic powders not only facilitate innovative manufacturing techniques but also pave the way for advancements in technology. As industries evolve, understanding the qualities and applications of various metallic powders will become increasingly vital for engineers and manufacturers aiming to optimize their projects and reduce costs.
In recent years, metallic powders have emerged as crucial components in various industrial applications, especially in additive manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive sectors. A comparative analysis of performance reveals that the different types of metallic powders—such as aluminum, titanium, and stainless steel—exhibit distinct properties that influence their utility in projects. According to a report by the International Journal of Powder Metallurgy, titanium powders demonstrate outstanding strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for aircraft components, where minimizing weight while maximizing strength is vital.
Furthermore, the latest findings from the Metal Powder Industries Federation indicate that aluminum powders are increasingly favored in 3D printing, particularly due to their excellent thermal conductivity and lightweight characteristics. This has significant implications for the automotive industry, where fuel efficiency is paramount. The study highlights that components produced using aluminum powders can reduce overall vehicle weight by up to 30%, leading to a substantial decrease in fuel consumption over the vehicle's lifespan. Meanwhile, stainless steel powders continue to dominate in applications requiring robust corrosion resistance, as reflected in the 2022 Additive Manufacturing Market Report, which notes a 20% increase in demand for stainless steel components across diverse industries.
As industries evolve, the performance of these metallic powders in various environments will shape future innovations and applications. Understanding their comparative advantages is key for engineers and manufacturers looking to optimize material selection for specific project requirements.
Handling metallic powders requires diligence and adherence to best practices to ensure safety and quality. When storing metallic powders, it is crucial to keep them in a cool, dry environment to prevent oxidation and degradation. Containers should be airtight and made of non-reactive materials to avoid contamination. Labeling storage containers clearly helps in identifying the contents easily and ensures proper handling procedures are followed.
During handling, it is essential to minimize dust generation, as fine metallic powders can be flammable and pose health risks when inhaled. Using proper personal protective equipment, such as gloves, goggles, and dust masks, can significantly reduce exposure. Additionally, implementing protocols for cleaning up spills, such as using appropriate vacuum systems designed for hazardous materials, helps maintain a safe working environment. Regular training on these practices can further reinforce safety and ensure that all personnel are equipped to handle metallic powders responsibly.