In the realm of 3D printing, stainless powder plays a pivotal role. This material enables the creation of robust metal parts with exceptional precision. The unique properties of stainless powder, such as its resistance to corrosion, make it ideal for various applications.
Metal 3D printing has evolved, yet challenges remain. The right parameters for using stainless powder can be elusive. Proper handling and preparation are crucial for achieving desired outcomes. Artists and engineers often face hurdles in mastering this technique. Some prints may not meet quality expectations, prompting a need for adjustment.
Understanding stainless powder's behavior is essential for improvement. Experimentation can lead to better results, but it also requires patience. Each attempt reveals more about the process. Ultimately, success hinges on diligence and learning from mistakes. Embracing these imperfections can lead to breakthroughs in metal 3D printing.
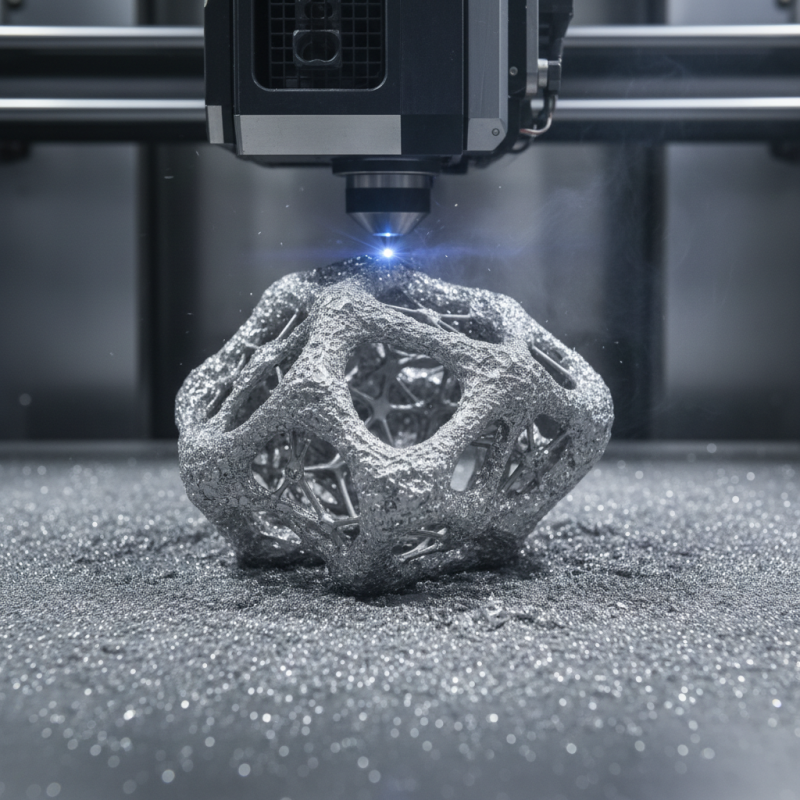

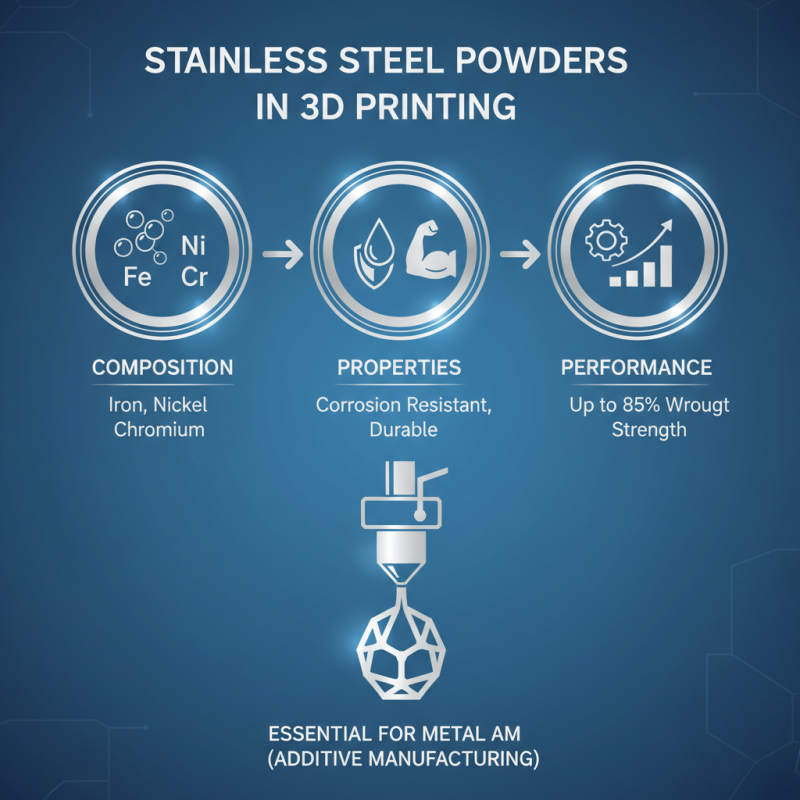
Stainless steel powders are essential in metal 3D printing. Their unique properties contribute to the overall performance of printed parts. These powders consist mainly of iron, nickel, and chromium, providing excellent corrosion resistance and durability. For instance, studies indicate that stainless steel parts show up to 85% of the strength of their wrought counterparts.
The process of 3D printing with stainless steel can present challenges. Proper particle size distribution is crucial. Typically, sizes range from 15 to 45 microns. A finer powder can enhance resolution but may interfere with flowability. This trade-off is vital for successful layer adhesion. Some failures in prints arise from suboptimal powder characteristics.
Density is another factor affecting print outcomes. The density of stainless steel powders can vary significantly. High-density powders are better for achieving thorough infill but may have higher costs. A quality density range is critical in predicting mechanical properties. Research by industry experts shows that a density reduction of 1% can affect tensile strength by approximately 2%. Understanding these nuances is vital for optimizing printing processes.
To prepare stainless steel powder for effective metal 3D printing, several key techniques must be considered. Particle size and distribution greatly influence flowability and sintering behavior. Research from industry experts indicates that an ideal particle size is typically between 20 and 60 microns. However, obtaining a uniform size distribution can be challenging. Larger agglomerates may cause inconsistencies in layering during the printing process.
Another critical aspect is the powder's moisture content. High moisture levels can lead to defects in the final print, such as reduced mechanical properties. According to data from recent studies, keeping moisture below 0.1% is ideal. However, achieving this level of dryness may require diligent powder handling practices. This can be difficult, especially in humid environments where powders tend to absorb moisture quickly.
Furthermore, the type of gas used in the atomization process can affect the powder's oxidation levels. Stainless steel powders should ideally be produced in an inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation. However, not all facilities maintain such environments, leading to variability in powder quality. Recognizing these challenges is essential for improving metal 3D printing outcomes and ensuring the reliability of the final products.
| Technique | Description | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powder Sizing | Ensure the stainless steel powder is within optimal size range (20-50 microns). | Improves flowability and packing density. | Requires careful screening and sorting processes. |
| Powder Blending | Blend different powder batches to achieve uniformity. | Enhances consistency in printing properties. | Monitor for contamination risks. |
| Sieving | Use sieves to remove oversized particles. | Prevents defects in printed parts. | Time-consuming process. |
| Moisture Control | Desiccate powder to remove moisture content. | Reduces the risk of oxidation and clumping. | Requires appropriate storage solutions. |
| Particle Morphology | Optimize the shape of powder particles for better flow. | Improves layer adhesion and print resolution. | Can be influenced by production methods. |
Stainless steel powders play a crucial role in 3D printing processes. The selection of the right binder is key. Recent studies indicate that certain organic binders can enhance print fidelity. For instance, a study published by the Journal of Materials Research showed a 20% improvement in part density using a specific polymer blend. This highlights the importance of optimizing binder composition.
Print parameters also heavily influence the outcome. Layer thickness can affect surface finish and mechanical properties. Many experts recommend a layer height between 50 to 100 microns to strike a balance between detail and print speed. Adjusting the print speed can lead to variations in thermal stability, impacting the final product. A slower speed may yield better precision, while a quicker approach often reduces production time.
However, achieving optimal results is often challenging. Some users report issues like poor layer adhesion or print warping. This can happen due to incorrect temperature settings. A temperature that's too low can lead to weak bonds. Data suggests that maintaining a consistent temperature during printing can improve structural integrity. Meticulous adjustments in parameters are necessary for successful prints.
Post-processing is crucial for enhancing stainless steel 3D printed parts. After the printing process, parts often show rough surfaces and residual powders. Techniques like sanding and polishing can help refine the finish.
Consider using different grit levels to achieve a smooth surface. Watch out, though; over-polishing may alter the dimensions of your parts.
Another effective method is heat treatment. This process can improve the mechanical properties of the part. It helps relieve internal stresses and increase strength. However, be cautious with temperature settings.
Too high a temperature can lead to warping or distortion. Testing on sample parts before final production is advisable.
Tips: Always wear protective gear during post-processing. This ensures safety from fine particles and sharp edges. Regularly check your tools for wear to maintain an efficient workflow.
Additionally, keep a log of each method you try. Reflecting on what works best can guide future projects. Post-processing requires patience and precision; it's not always a quick fix.
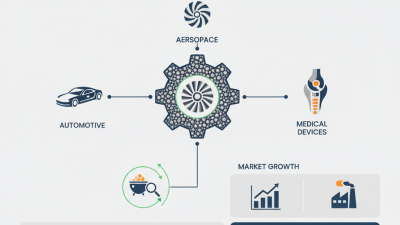
Stainless steel metal 3D printing is growing rapidly. According to a recent industry report, the market is projected to reach $2.5 billion by 2027. This growth is driven by diverse applications, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical technologies. Companies increasingly prefer stainless steel for its corrosion resistance and strength. However, challenges remain.
A major factor is the quality of the powder. Not all stainless powders are the same. Poor-quality powder may lead to structural weaknesses in printed parts. This can affect performance and safety. It’s crucial to source high-quality materials to avoid costly failures.
**Tips:** Always evaluate the particle size distribution of the powder. A narrower distribution often results in better layer adhesion. Experiment with different print settings to optimize results.
Additionally, monitoring thermal properties during printing is essential. Variations in temperature can cause defects. Even slight changes can lead to imperfections. There’s always room for improvement in process control and quality assurance.
**Tips:** Invest in advanced monitoring tools. They can help maintain consistent temperatures throughout printing. Regularly reviewing print data can reveal patterns for better outcomes.