Weld Metal Powder is a crucial component in modern welding processes. It plays a significant role in creating durable and high-quality joints. This material is used primarily in specialized welding techniques, making it essential for various industries. The powder is designed to enhance the weld's properties, ensuring strength and resistance.
In practical applications, Weld Metal Powder is blended with other materials. This ensures optimal performance during welding. Its size and composition can vary, impacting the final product's quality. The right choice of powder can make a difference in efficiency and effectiveness. However, not all powders are suitable for every situation. Some might fall short, leading to weaker welds.
Weld Metal Powder can be perceived as an art and a science. The balance between quality and cost is often challenging. Often, individuals overlook the importance of selecting the right powder. This can result in less than ideal outcomes. As technology evolves, understanding these materials becomes increasingly vital. Knowledge of Weld Metal Powder allows welders to make informed decisions for better results.

Weld metal powder is a crucial component in additive manufacturing and welding processes. It consists of fine metal particles designed for use in various welding applications. This powder guarantees a strong bond between materials during welding. Often made from alloys or pure metals, it provides flexibility in creating diverse joints.
According to industry reports, the global market for weld metal powder is projected to grow significantly. In 2021, it was valued at approximately $1.2 billion and is expected to reach around $2 billion by 2026. Factors driving this growth include the increasing demand for advanced manufacturing techniques and the rising need for lightweight materials in various industries.
Challenges exist in the production and application of weld metal powder. Contamination can compromise quality. Precise control of particle size is essential, as variations can lead to inconsistent weld properties. As companies push for efficiency, they face the risk of producing subpar materials. Continuous improvement in powder metallurgy techniques is necessary to overcome these obstacles.
Weld metal powder is a critical component in various welding processes. Its composition primarily includes alloys of metals, such as iron, nickel, or chromium. These powders are designed to melt during welding, forming a solid joint once they cool. Key properties of weld metal powder include its melting point, flowability, and particle size. These factors greatly influence the welding performance and the quality of the final joint.
The microstructure of weld metal powder can vary significantly based on its composition. This impacts the mechanical properties of the weld. For example, a powder with a higher percentage of nickel may offer better corrosion resistance. On the other hand, it might also lead to brittleness in certain conditions. Some users may find it challenging to achieve the desired balance. Fine-tuning these aspects requires both knowledge and experience from the operator.
In practice, the selection of weld metal powder must consider the specific application. Different projects may demand distinct characteristics. Using the wrong type can lead to subpar results. This is a point of reflection for many welders. It's essential to continually assess the materials used and their performances. A small oversight can have significant consequences in the field.
Weld metal powder plays a vital role in various industries. It is used primarily in additive manufacturing processes. This involves layering materials to create robust components. The powder can be made from various metals, each offering unique properties.
In the aerospace industry, weld metal powder is essential for creating lightweight structures. These components must withstand extreme conditions. The ability to customize the composition of the powder improves performance. However, achieving optimal properties can be tricky. Careful adjustments in the production process are needed.
Another sector benefiting from weld metal powder is automotive manufacturing. This material allows for stronger, more durable parts. Weld metal can enhance traditional welding techniques. Yet, there is a learning curve for engineers to master. Experimentation is crucial to find the best applications and methods. The challenges in perfecting these techniques can be significant.
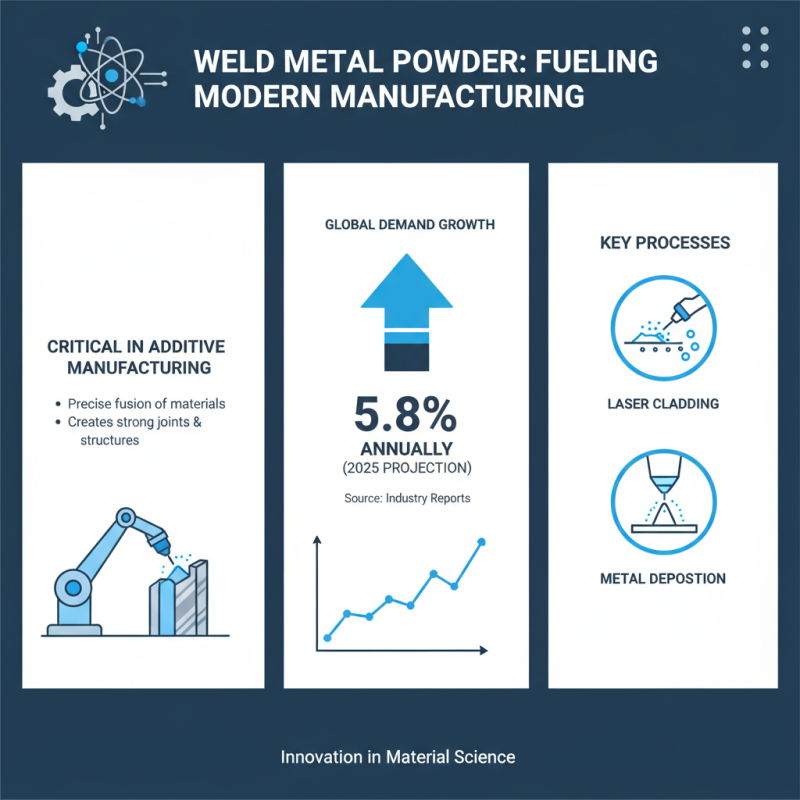
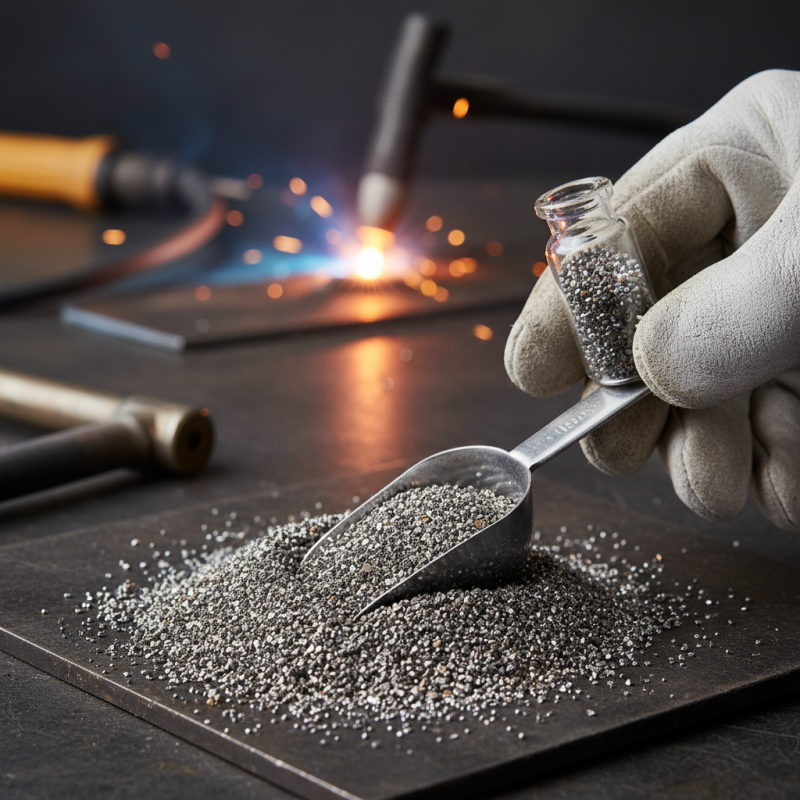
Weld metal powder is vital in modern manufacturing, especially for additive processes. This powder allows for precise fusion of materials, creating strong joints and structures. According to industry reports, the global demand for weld metal powder is expected to grow at a rate of 5.8% annually up to 2025. It is a critical component in processes such as laser cladding and metal deposition.
In laser cladding, weld metal powder is applied as a layer over a substrate. This technique enhances surface properties, making parts more resistant to wear and corrosion. The accuracy of laser cladding using weld metal powder can achieve thicknesses as small as 0.5 mm. However, there are challenges. Achieving a consistent layer may require extensive calibration. In some cases, the heat input can lead to warping or distortion of the base material.
Another notable process is selective laser melting (SLM). In SLM, weld metal powder is fully melted to create intricate shapes. This method allows for lightweight designs while maintaining mechanical strength. Yet, it is not without issues. Powder quality impacts the final result significantly. Variability in grain size can lead to defects. Thus, ensuring uniformity in the powder is crucial for effective production.
Weld metal powder is a crucial material in welding processes, especially in additive manufacturing. It offers unique benefits, but challenges also arise. One significant benefit is its versatility. According to industry reports, around 70% of manufacturers opt for metal powder in high-precision applications. This flexibility allows for various welding techniques, enabling complex geometries and superior mechanical properties.
However, using weld metal powder presents challenges. The quality of the powder greatly impacts the final weld. Contaminants can lead to defects. A study revealed that 15% of weld failures were linked to poor-quality powders. Additionally, handling and storage are critical. The hygroscopic nature of certain powders makes them prone to moisture absorption, affecting performance. Regular assessment is required to maintain powder integrity.
Another challenge is the cost. Quality metal powders can be expensive, and not all projects justify this investment. Moreover, the learning curve for operators can be steep, leading to potential errors. Striking a balance between cost and quality becomes essential for many organizations.
| Dimension | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Weld metal powder is a fine metallic powder used in various welding processes to facilitate fusion and improve weld quality. |
| Common Applications | Used in laser cladding, hardfacing, and metal additive manufacturing. |
| Benefits | 1. Enhanced mechanical properties 2. Reduced thermal distortion 3. Ability to create complex geometries |
| Challenges | 1. High initial cost 2. Requires specialized equipment 3. Sensitivity to contamination |
| Materials Used | Common alloys include steel, nickel, titanium, and cobalt. |
| Post-Weld Treatment | Often requires heat treatment or machining for optimal performance. |
| Environmental Considerations | Dust generated can be a health hazard; proper safety measures are necessary. |