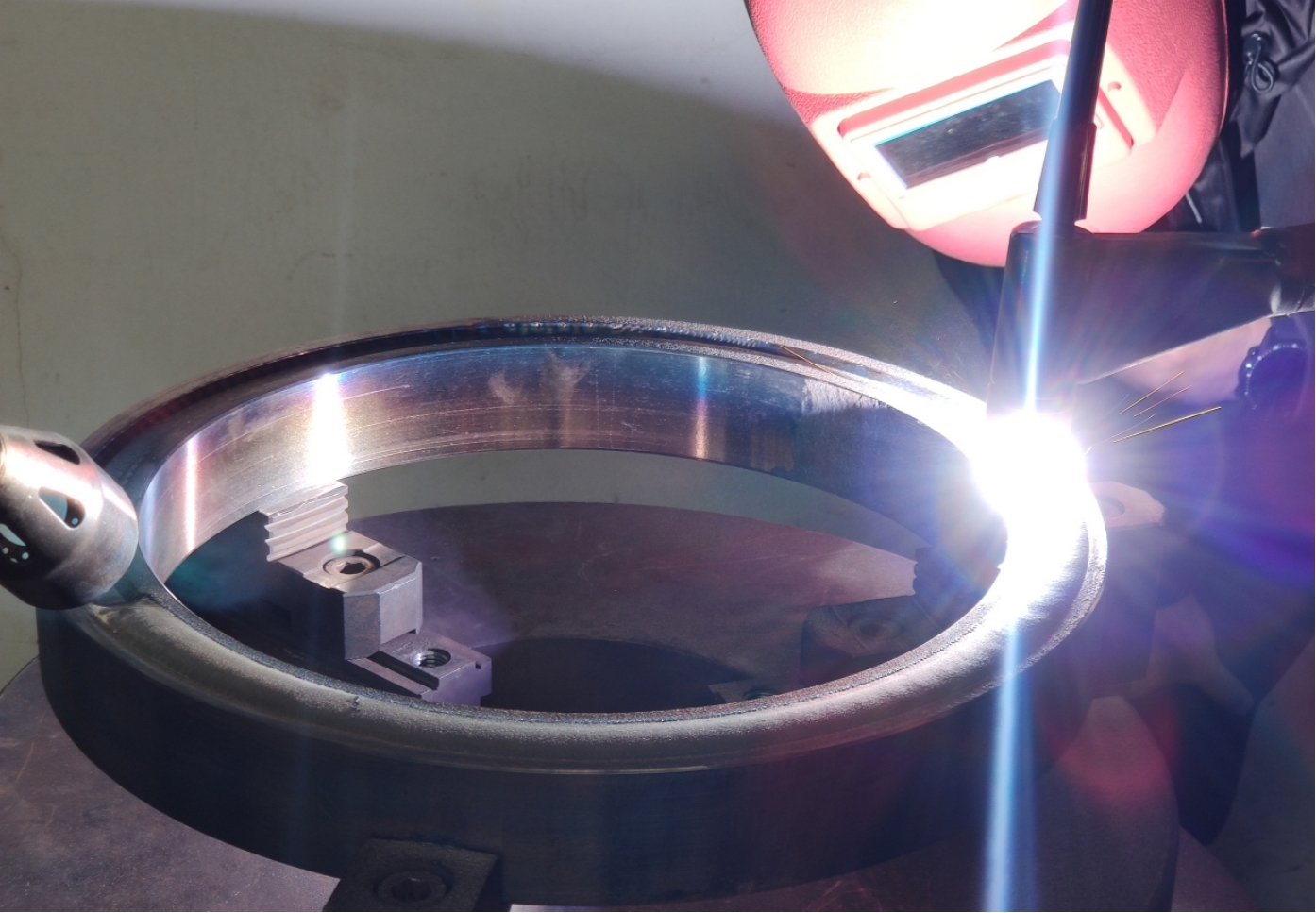
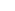What are the applications of tungsten carbide coatings produced by high velocity oxygen fuel spraying?
Tungsten carbide coatings produced by high velocity oxygen fuel spraying (HVOF) have been widely and maturely applied in numerous industrial fields due to their excellent performance. The following are some of the main application areas, which are presented in a natural way:
1. Aerospace:
Critical component protection: Widely used in key aircraft engine components such as compressor blades, turbine blade tenons, seal rings, journals, and landing gear components. The coating provides excellent wear resistance, effectively resisting air erosion, fretting wear, and foreign object damage, significantly extending component life and improving engine reliability and safety (such as components related to the CFM56 engine).
Aircraft components: Used in helicopter transmission system components (such as gear shafts) and rotor components to resist wear under high loads.
2. Oil and Gas Industry:
Drilling and completion tools: Used in key components such as drill collars, centralizers, downhole motor rotors/stators, drill bit gauges, mud pump liners, and valve seats and valve cores. The coating protects against severe erosion and wear from formation sand and debris, as well as slurry corrosion, reducing non-productive time and lowering maintenance costs.
Downhole Tools: Improves the wear resistance and seal life of tools such as packer slips, sleeves, and choke valves.
Pipes and Valves: Prevents erosion on pipe elbows, tees, and valve sealing surfaces used to transport fluids containing solid particles.
3. Energy and Power Industry:
Hydropower: Applied to flow components such as turbine blades, guide vanes, wear plates, and seal rings to protect against severe erosion and cavitation damage from high-velocity, sand-laden water.
Coal/Gas-fired Power Generation: Applied to boiler piping (such as reheater and superheater tubes), fan blades (induced draft fans, dust collectors), and valve components, improving wear resistance and providing some corrosion resistance.
Nuclear Power: Applied to pump shafts, valves, and other components requiring high wear resistance, within permitted non-core areas.
4. Industrial Manufacturing and Machinery:
Pump Equipment: Widely used in impellers, seals, bushings, and pump casing flow areas of various industrial pumps (centrifugal pumps, slurry pumps, and chemical pumps), significantly improving wear resistance and life, especially when conveying abrasive media.
Compressor Components: Used on compressor piston rods, plungers, vanes, and blades to reduce friction and wear.
Hydraulic Systems: Used on hydraulic cylinder piston rods, providing excellent wear and corrosion resistance and a low-friction surface, extending seal life.
Papermaking Machinery: Used on dryer journals, guide rollers, refiner discs, vacuum chamber panels, and other applications to resist wear and corrosion.
Textile Machinery: Used on godet rollers, rollers, and rings, among other high-wear components.
Molds and Tools: Used on injection mold ejectors, guide pins and bushings, extrusion screws, and die-casting mold cores, improving wear resistance and demolding performance, thereby extending mold life.
Rollers and Roller Parts: Used for repairing and strengthening the journals or roller surfaces of various types of rollers (such as straightening rollers and conveyor rollers).
5. Transportation:
Automotive Industry: Used in engine valve lifters, piston rings (in some applications), transmission components (such as synchronizer rings), shock absorber piston rods, etc., to improve wear resistance.
Shipbuilding Industry: Used in ship diesel engine piston rings, cylinder liners (in some applications), stern shafts, seawater pump impellers, etc., to resist wear and seawater corrosion.
6. Other Industries:
Medical Devices (Non-Implantable): Used in surgical instruments (such as orthopedic drills and reamers) and dental tools, etc., requiring extremely high wear resistance and a certain degree of biocompatibility.
3C Electronics Manufacturing: Used in the surfaces of cutting tools, molds, and fixtures used in processing hard and brittle materials such as glass and sapphire, to improve wear resistance and product yield.
Construction Machinery: Used in excavator bucket teeth (reinforced parts), blades, hydraulic rods, etc.
Summary of its core advantages and application drivers:
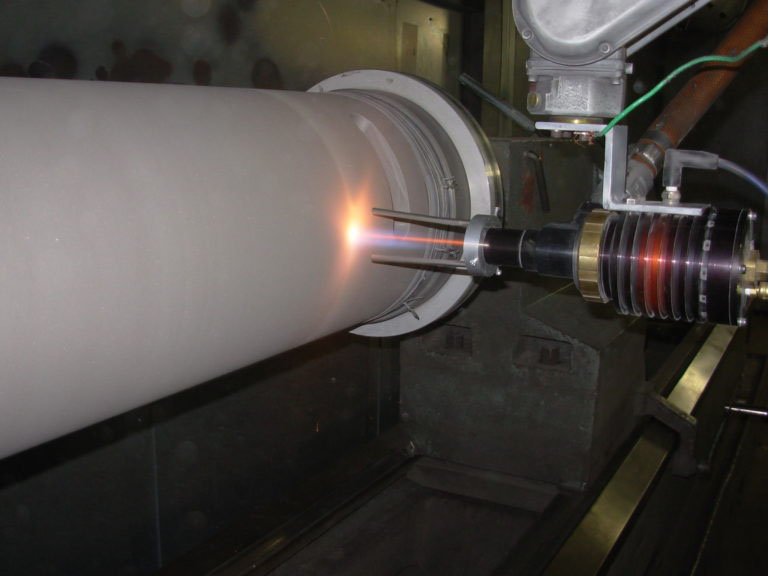
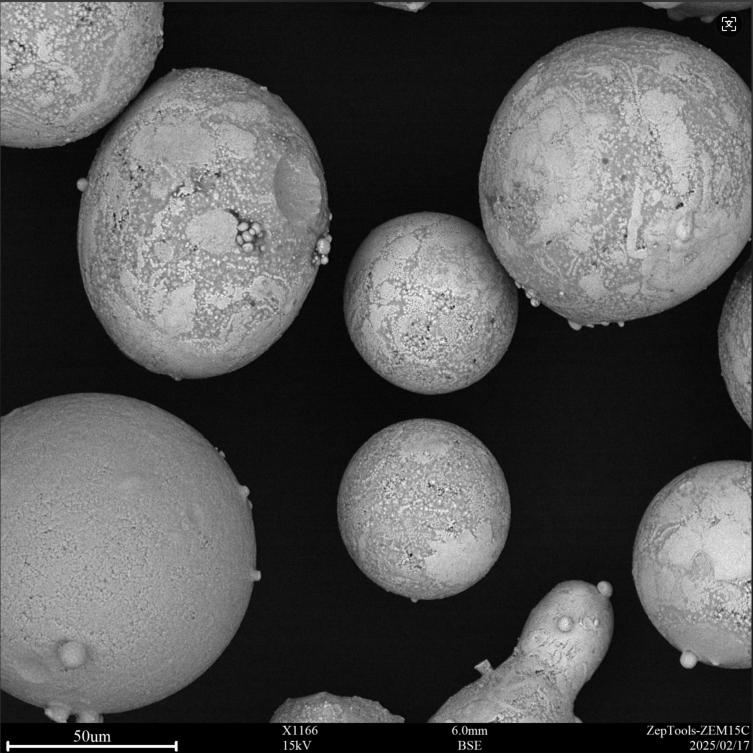
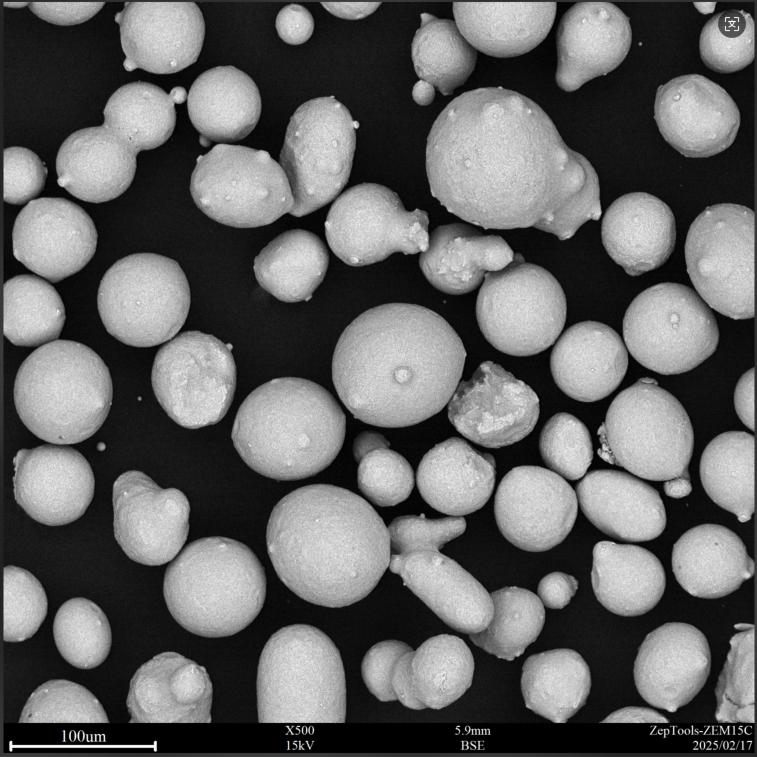
Excellent wear resistance: Its strong resistance to sliding wear, abrasive wear, erosion wear, and fretting wear is the fundamental reason for its widespread application. High hardness combined with good toughness: HVOF coatings are dense, have low porosity (typically <1%), and offer high bonding strength, resisting spalling under impact and fatigue loads.
Excellent corrosion resistance (especially when combined with a cobalt base): Effectively resists corrosion from a wide range of media in non-extreme chemical environments.
Machinability: The coating can be ground, lapped, or polished to precise dimensions and finish requirements.
Excellent tribological properties: Commonly used for wear-resistant seals or low-friction surfaces.
These applications fully demonstrate the value of HVOF tungsten carbide coatings as a mature and reliable surface enhancement technology in addressing wear and corrosion failures in critical industrial components, extending equipment life, and improving operational reliability and economic efficiency. It is particularly valuable in applications requiring long-term resistance to harsh wear environments.